Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 16:33 — 7.6MB) | Embed
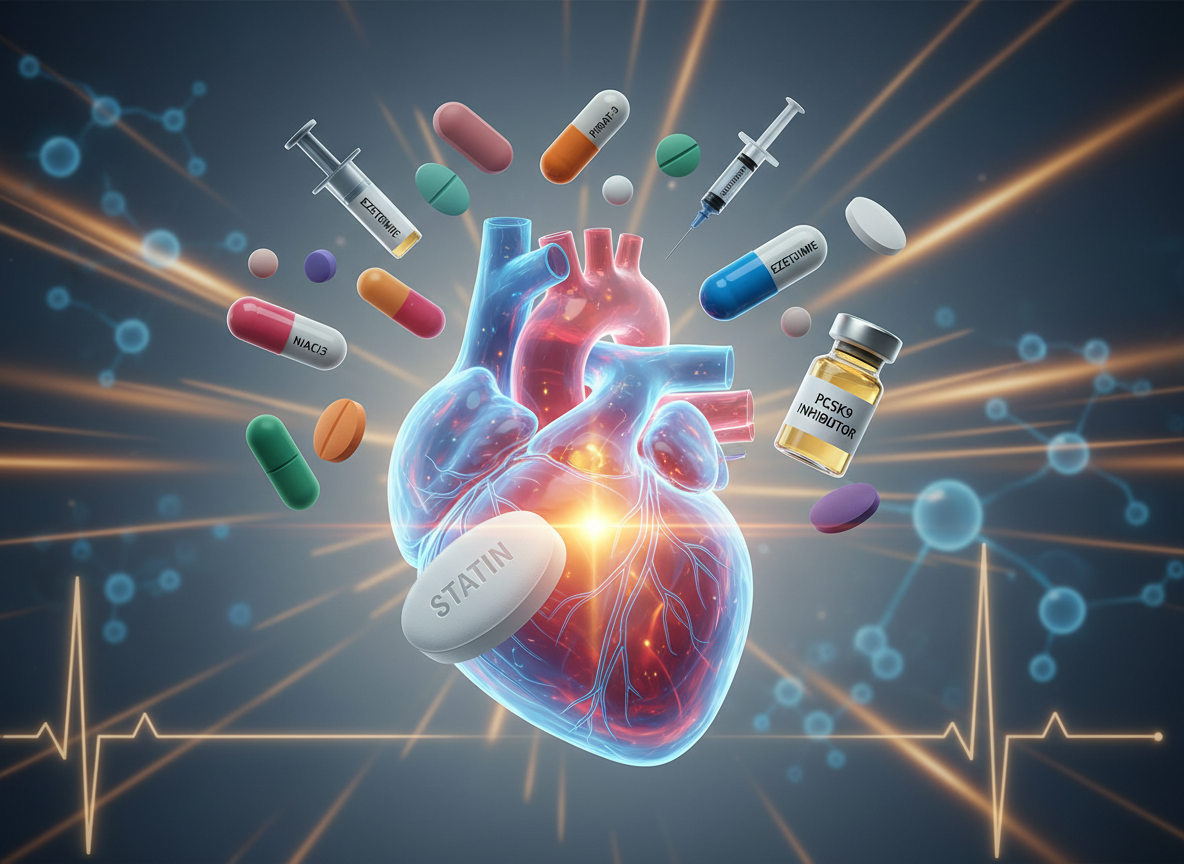
On this podcast episode, I discuss important practice pearls and important test prep information about statins. Statins are cornerstone agents for ASCVD risk reduction, so test questions often focus on indication, intensity, and monitoring. Health care professionals should quickly identify statin intensity: high-intensity therapy (atorvastatin 40–80 mg, rosuvastatin 20–40 mg) lowers LDL by ~50% and is indicated for patients with clinical ASCVD, LDL ≥190 mg/dL, or high-risk diabetes patients age 40–75. Moderate-intensity statins (e.g., atorvastatin 10–20 mg, simvastatin 20–40 mg) are commonly tested for primary prevention.
Statin-associated muscle symptoms range from myalgias (most common, normal CK) to rare but serious rhabdomyolysis (marked CK elevation and AKI). Risk factors include high doses, advanced age, hypothyroidism, drug interactions, and renal impairment. If muscle symptoms occur, stopping the statin, ruling out secondary causes (like hypothyroidism), and rechallenging with a lower dose or different statin is often the correct clinical approach.
Drug interactions and statin selection frequently separate good from great test-takers. Lipophilic statins (simvastatin, atorvastatin, lovastatin) are more prone to muscle effects and CYP3A4 interactions, while hydrophilic statins (pravastatin, rosuvastatin) are preferred in patients with prior intolerance or complex drug regimens. Grapefruit juice, strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, and certain calcium channel blockers raise simvastatin levels—often prompting dose limits or avoidance on exams. If LDL goals aren’t met, adding ezetimibe or a PCSK9 inhibitor is the next evidence-based step.
Be sure to check out our free Top 200 study guide – a 31 page PDF that is yours for FREE!
Support The Podcast and Check Out These Amazing Resources!
Meded101 Guide to Nursing Pharmacology (Amazon Highly Rated)
Guide to Drug Food Interactions (Amazon Best Seller)