Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 12:41 — 17.4MB) | Embed
On this episode I discuss colchicine pharmacology, adverse effects, drug interactions, and pharmacokinetics.
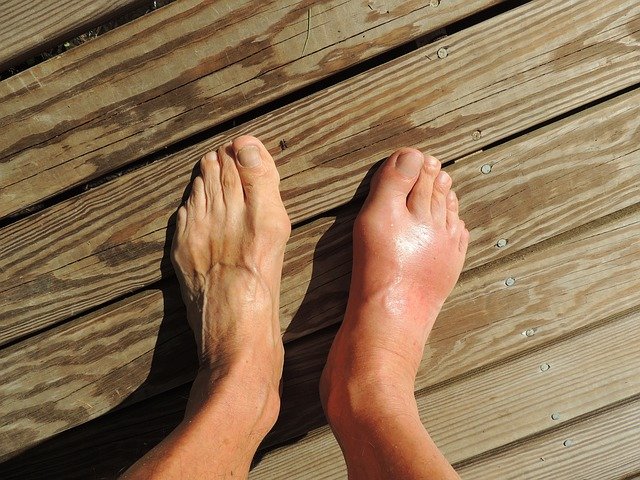
Colchicine ultimately works by reducing the activity of neutrophils that help contribute to pain and inflammation associated with gout.
Colchicine does have some drug interactions with medications and grapefruit juice via CYP3A4.
The most common dose limiting side effect of colchicine is diarrhea.
Colchicine can be used as a potential alternative to NSAIDs or corticosteroids in the management of a gout flare.
Be sure to check out our free Top 200 study guide – a 31 page PDF that is yours for FREE!